How to Reduce Query Memory Usage in ClickHouse: Troubleshooting Memory Limit Exceeded Errors
Memory limit exceeded errors are among the most common challenges ClickHouse users face when running complex analytical queries. Whether you’re performing large aggregations, executing heavy joins, or processing massive datasets, understanding how to manage and optimize memory usage is crucial for maintaining query performance and system stability.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through proven strategies to troubleshoot and resolve memory limit exceeded errors in ClickHouse, covering configuration settings, external aggregation techniques, memory-efficient functions, and profiling tools.
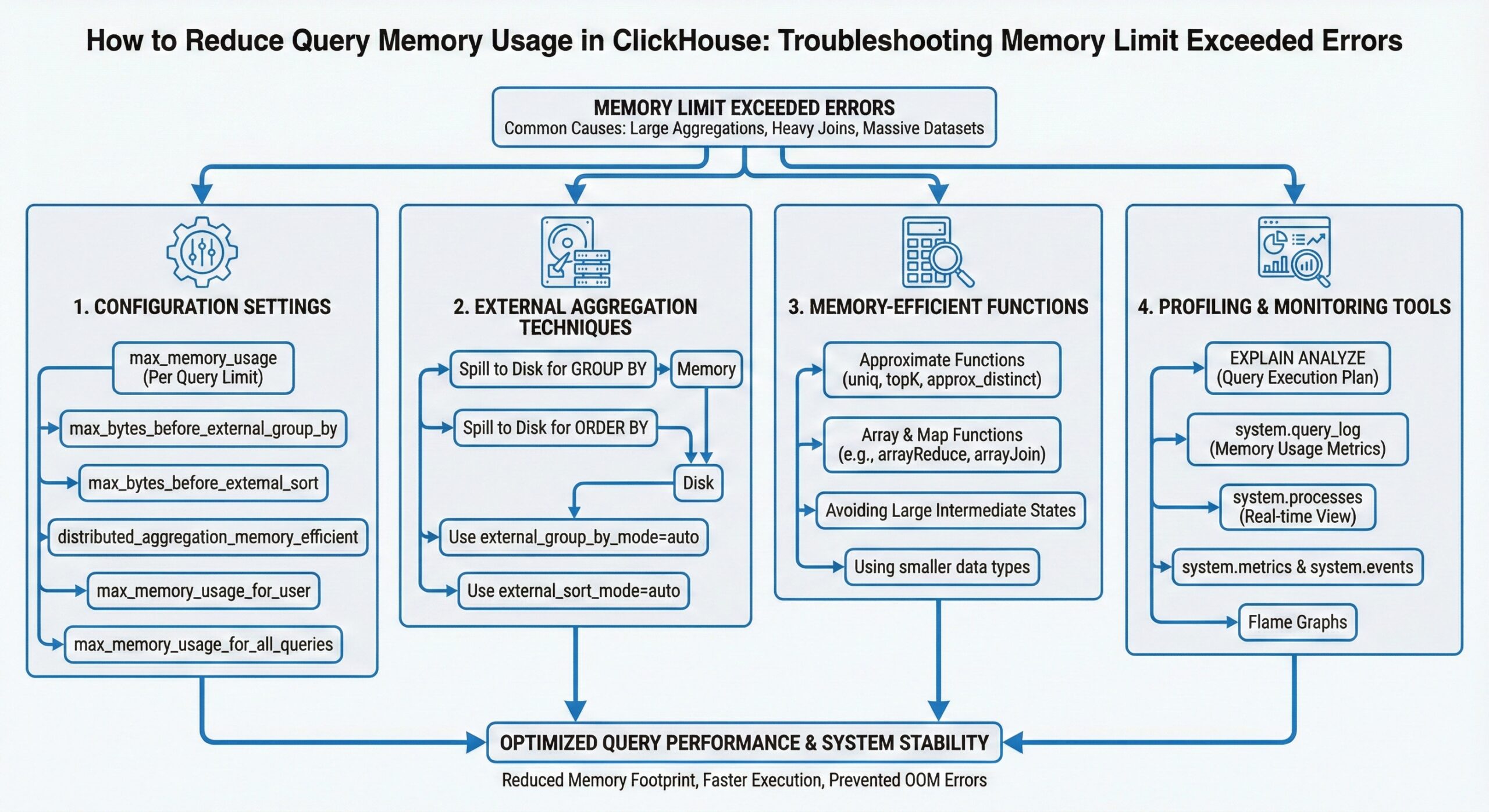
Understanding Memory Limit Exceeded Errors
When ClickHouse encounters a memory limit exceeded error, it means a query has attempted to consume more RAM than allocated. These errors typically occur during:
- Large aggregations with high cardinality GROUP BY operations
- Complex joins involving multiple large tables
- Sorting operations on substantial datasets
- Subqueries that materialize large intermediate results
The key to resolving these issues lies in understanding ClickHouse’s memory management settings and implementing appropriate optimization strategies.4
Configuring max_memory_usage
The max_memory_usage setting is your first line of defense against runaway queries. This parameter defines the maximum amount of RAM a single query can consume on a server.1
Setting Memory Limits
You can configure max_memory_usage at multiple levels:
Session Level:
SET max_memory_usage = 10000000000; -- 10 GB
User Level:
-- Set in users.xml or via SQL ALTER USER clickhouse_user SETTINGS max_memory_usage = 10000000000;
Query Level:
SELECT * FROM large_table SETTINGS max_memory_usage = 5000000000;
Best Practices for max_memory_usage
- Start conservative: Begin with lower limits and increase as needed
- Monitor system resources: Ensure total memory allocation across concurrent queries doesn’t exceed available RAM
- Consider query patterns: Adjust limits based on typical query complexity
- Use constraints: Implement minimum and maximum bounds to prevent misconfiguration8
The max_memory_usage_for_user setting provides an additional layer of control by limiting total memory consumption across all queries from a specific user.3
Leveraging External Aggregation
When queries require more memory than available RAM, external aggregation allows ClickHouse to spill data to disk, preventing memory limit errors while maintaining query functionality.
Configuring max_bytes_before_external_group_by
The max_bytes_before_external_group_by setting determines when GROUP BY operations should start writing temporary data to the filesystem instead of keeping everything in memory.2
SET max_bytes_before_external_group_by = 20000000000; -- 20 GB
When this threshold is reached, ClickHouse automatically:
- Flushes aggregation data to temporary disk storage
- Continues processing with reduced memory footprint
- Merges results from disk and memory at query completion
External Sorting Configuration
Similarly, for sorting operations:
SET max_bytes_before_external_sort = 20000000000;
Performance Considerations
While external aggregation prevents memory errors, it comes with trade-offs:12
- Slower query execution: Disk I/O is significantly slower than RAM operations
- Increased disk usage: Ensure adequate temporary storage space
- I/O contention: Multiple concurrent queries using external aggregation can strain disk subsystems
Optimization tip: Use external aggregation as a safety mechanism rather than a primary strategy. Optimize queries and data structures first to minimize memory requirements.
Distributed Aggregation Memory Efficiency
For distributed queries, enable memory-efficient aggregation:
SET distributed_aggregation_memory_efficient = 1;
This setting reduces memory consumption during distributed GROUP BY operations by processing data in smaller chunks.6
Memory-Efficient Aggregate Functions
Choosing the right aggregate functions can dramatically reduce memory consumption, especially when dealing with high-cardinality data.
uniqCombined: The Memory-Efficient Choice
The uniqCombined function is specifically designed for memory-efficient distinct counting:1116
SELECT uniqCombined(user_id) FROM events;
How uniqCombined works:
- Small sets: Uses an array for exact counting
- Medium sets: Transitions to a hash table
- Large sets: Switches to HyperLogLog algorithm with fixed memory usage
Advantages over uniq():16
- Consumes several times less memory
- Provides higher accuracy for large datasets
- Fixed memory footprint regardless of cardinality
- Better suited for distributed aggregations
Memory Usage Comparison
-- Memory-intensive approach SELECT uniq(high_cardinality_column) FROM large_table; -- Memory-efficient approach SELECT uniqCombined(high_cardinality_column) FROM large_table;