Mastering Nested JOINs in ClickHouse: A Complete Guide to Embedding JOINs within JOINs
ClickHouse’s powerful JOIN capabilities allow for complex data relationships through nested JOIN operations. Understanding how to embed JOINs within JOINs is crucial for advanced analytics and data warehousing scenarios.
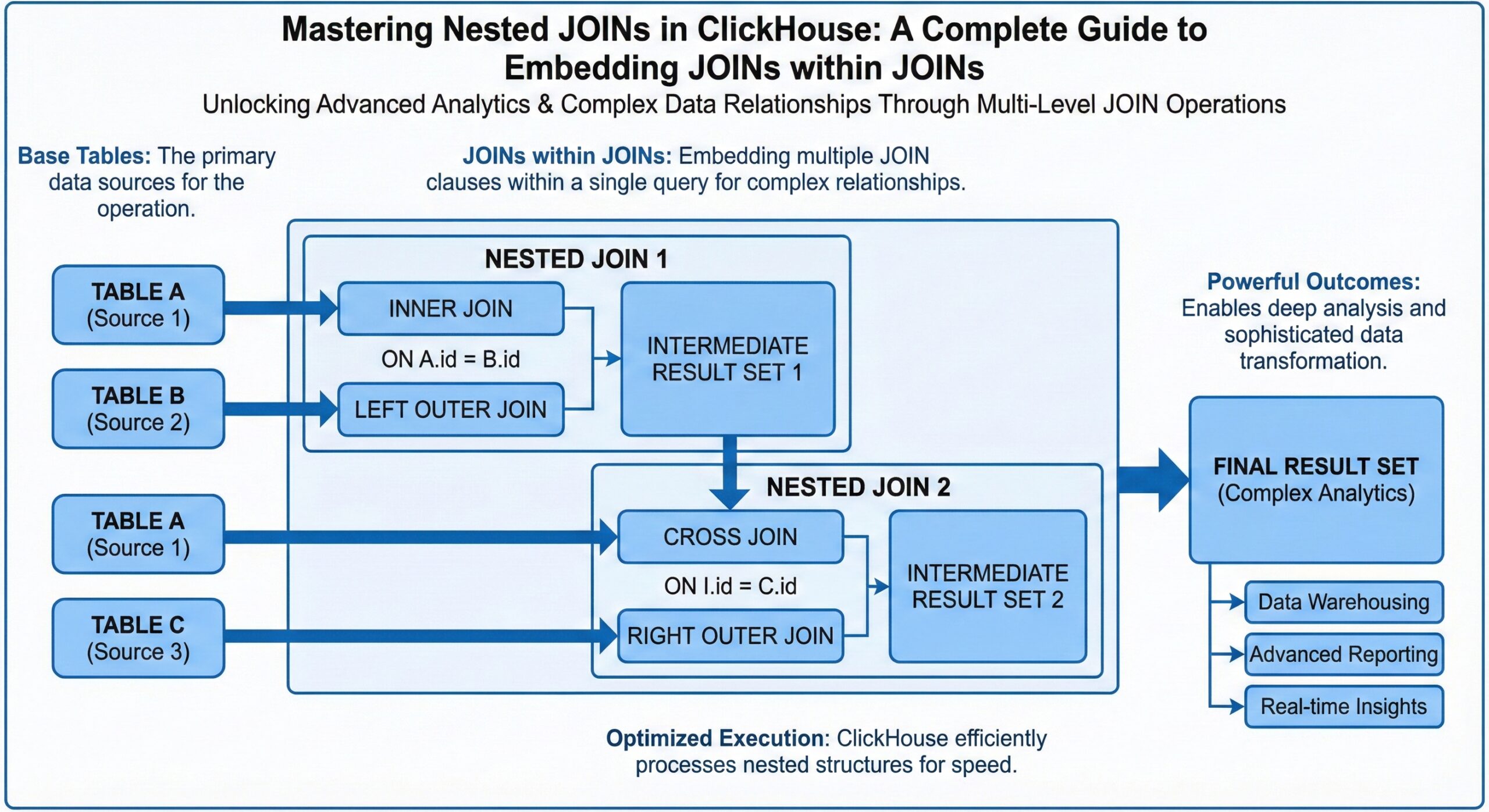
Understanding JOIN Nesting in ClickHouse
ClickHouse supports multiple JOIN types that can be nested to create sophisticated query patterns. The key is understanding execution order and performance implications.
-- Basic nested JOIN structure
SELECT
a.id,
a.name,
b.category,
c.region,
d.sales_amount
FROM table_a a
JOIN (
SELECT * FROM table_b
WHERE active = 1
) b ON a.category_id = b.id
JOIN (
SELECT region_id, region_name as region
FROM regions r
JOIN countries c ON r.country_id = c.id
WHERE c.active = 1
) c ON a.region_id = c.region_id
LEFT JOIN sales_data d ON a.id = d.product_id
Advanced Nested JOIN Patterns
Multi-Level Subquery JOINs
-- Complex nested JOIN with aggregations
SELECT
main.product_id,
main.product_name,
category_stats.avg_price,
regional_data.total_sales
FROM products main
JOIN (
-- Nested JOIN for category statistics
SELECT
c.id as category_id,
c.name as category_name,
avg(p.price) as avg_price
FROM categories c
JOIN (
SELECT category_id, price
FROM products
WHERE status = 'active'
) p ON c.id = p.category_id
GROUP BY c.id, c.name
) category_stats ON main.category_id = category_stats.category_id
LEFT JOIN (
-- Nested JOIN for regional sales data
SELECT
s.product_id,
sum(s.amount) as total_sales
FROM sales s
JOIN (
SELECT store_id, region_id
FROM stores st
JOIN regions r ON st.region_id = r.id
WHERE r.active = 1
) store_regions ON s.store_id = store_regions.store_id
GROUP BY s.product_id
) regional_data ON main.product_id = regional_data.product_id
Common Table Expressions with Nested JOINs
-- Using WITH clauses for better readability
WITH
active_categories AS (
SELECT c.id, c.name, avg(p.price) as avg_price
FROM categories c
JOIN products p ON c.id = p.category_id
WHERE p.status = 'active'
GROUP BY c.id, c.name
),
regional_sales AS (
SELECT
s.product_id,
r.region_name,
sum(s.amount) as total_sales
FROM sales s
JOIN stores st ON s.store_id = st.id
JOIN regions r ON st.region_id = r.id
GROUP BY s.product_id, r.region_name
)
SELECT
p.id,
p.name,
ac.avg_price,
rs.total_sales,
rs.region_name
FROM products p
JOIN active_categories ac ON p.category_id = ac.id
LEFT JOIN regional_sales rs ON p.id = rs.product_id
Performance Optimization Strategies
JOIN Order Optimization
-- Optimized JOIN order - smallest tables first
SELECT *
FROM (
SELECT id, name FROM small_lookup_table
WHERE active = 1
) lookup
JOIN (
SELECT product_id, category_id, price
FROM large_products_table
WHERE price > 100
) products ON lookup.id = products.category_id
JOIN (
SELECT product_id, sum(quantity) as total_qty
FROM massive_sales_table
WHERE date >= '2024-01-01'
GROUP BY product_id
) sales ON products.product_id = sales.product_id
Using PREWHERE for Better Performance
-- Leveraging PREWHERE in nested JOINs
SELECT
p.product_name,
category_data.category_name,
sales_summary.total_revenue
FROM products p
JOIN (
SELECT
c.id,
c.name as category_name,
count(*) as product_count
FROM categories c
JOIN products sub_p ON c.id = sub_p.category_id
PREWHERE sub_p.created_date >= '2024-01-01'
GROUP BY c.id, c.name
) category_data ON p.category_id = category_data.id
LEFT JOIN (
SELECT
product_id,
sum(amount) as total_revenue
FROM sales
PREWHERE sale_date >= '2024-01-01'
GROUP BY product_id
) sales_summary ON p.id = sales_summary.product_id
PREWHERE p.status = 'active'
Real-World Use Cases
E-commerce Analytics
-- Product performance across regions and categories
SELECT
product_analysis.product_name,
product_analysis.category_name,
product_analysis.avg_rating,
regional_performance.region_name,
regional_performance.total_sales,
regional_performance.order_count
FROM (
SELECT
p.id as product_id,
p.name as product_name,
c.name as category_name,
avg(r.rating) as avg_rating
FROM products p
JOIN categories c ON p.category_id = c.id
LEFT JOIN (
SELECT product_id, rating
FROM reviews
WHERE created_date >= now() - INTERVAL 90 DAY
) r ON p.id = r.product_id
GROUP BY p.id, p.name, c.name
) product_analysis
JOIN (
SELECT
oi.product_id,
reg.name as region_name,
sum(oi.price * oi.quantity) as total_sales,
count(DISTINCT o.id) as order_count
FROM order_items oi
JOIN orders o ON oi.order_id = o.id
JOIN (
SELECT u.id as user_id, r.name
FROM users u
JOIN regions r ON u.region_id = r.id
) reg ON o.user_id = reg.user_id
WHERE o.created_date >= now() - INTERVAL 30 DAY
GROUP BY oi.product_id, reg.name
) regional_performance ON product_analysis.product_id = regional_performance.product_id
Financial Data Analysis
-- Multi-dimensional financial reporting
WITH account_hierarchy AS (
SELECT
a.id,
a.account_number,
a.account_name,
dept.department_name,
comp.company_name
FROM accounts a
JOIN departments dept ON a.department_id = dept.id
JOIN companies comp ON dept.company_id = comp.id
),
transaction_summary AS (
SELECT
t.account_id,
sum(CASE WHEN t.type = 'debit' THEN t.amount ELSE 0 END) as total_debits,
sum(CASE WHEN t.type = 'credit' THEN t.amount ELSE 0 END) as total_credits,
count(*) as transaction_count
FROM transactions t
JOIN (
SELECT id FROM transaction_batches
WHERE status = 'processed' AND batch_date >= '2024-01-01'
) tb ON t.batch_id = tb.id
GROUP BY t.account_id
)
SELECT
ah.company_name,
ah.department_name,
ah.account_name,
ts.total_debits,
ts.total_credits,
ts.total_credits - ts.total_debits as net_balance,
ts.transaction_count
FROM account_hierarchy ah
LEFT JOIN transaction_summary ts ON ah.id = ts.account_id
ORDER BY ah.company_name, ah.department_name, ah.account_name
Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
Memory Management
-- Use LIMIT in subqueries to control memory usage
SELECT *
FROM large_table lt
JOIN (
SELECT TOP 1000 id, category_id, price
FROM products
ORDER BY created_date DESC
) recent_products ON lt.product_id = recent_products.id
Index Utilization
-- Ensure JOIN conditions use indexed columns
SELECT *
FROM table_a a
JOIN (
SELECT indexed_column, data_column
FROM table_b
WHERE indexed_column IN (
SELECT id FROM filtered_ids WHERE condition = 'value'
)
) b ON a.foreign_key = b.indexed_column -- indexed_column should have an index
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Memory Exhaustion
- Use LIMIT clauses in subqueries
- Implement proper filtering with WHERE and PREWHERE
- Consider breaking complex queries into multiple steps
Performance Degradation
- Analyze query execution plans using EXPLAIN
- Ensure proper indexing on JOIN columns
- Use appropriate JOIN types (INNER, LEFT, RIGHT)
- Consider materialized views for frequently accessed nested JOIN patterns
Conclusion
Embedding JOINs within JOINs in ClickHouse enables powerful analytical capabilities but requires careful consideration of performance implications. By following these patterns and best practices, you can build efficient, maintainable queries that scale with your data growth.
Remember to always test query performance with realistic data volumes and monitor resource usage in production environments.
Further Reading:
- Understanding the OpenTelemetry Collector: A Comprehensive Guide to Modern Telemetry Management
- Building a Medallion Architecture with ClickHouse: A Complete Guide
- Mastering Custom Partitioning Keys in ClickHouse: A Complete Guide
- Why is ClickHouse So Fast? The Architecture Behind Lightning-Speed Analytics
- An Introduction to Time-Series Databases: Powering Modern Data-Driven Applications
- Nested Loop JOINs in MySQL
You might also like:
- Gen AI with LLM integration: Part 2 – Integrating ChatGPT with ChistaDATA DBaaS: A New Era of Intuitive Database Management
- ClickHouse October 2022 Release – v22.10
- Decoding Memory Management in ClickHouse
- ClickHouse May 2024 Release – v24.6
- ClickHouse Troubleshooting: Why is ClickHouse Index Underutilized?


